Pharmacovigilance GVP Modules: Everything You Need To Know To Earn $53,988 Per Year.
Best Choices
-
 Product on saleICSR Pharmacovigilance | Individual Case Safety Report Online TrainingOriginal price was: 59 $.19 $Current price is: 19 $.
Product on saleICSR Pharmacovigilance | Individual Case Safety Report Online TrainingOriginal price was: 59 $.19 $Current price is: 19 $. -
 Product on salePharmacovigilance PDF MaterialsOriginal price was: 299 $.49 $Current price is: 49 $.
Product on salePharmacovigilance PDF MaterialsOriginal price was: 299 $.49 $Current price is: 49 $.
Pharmacovigilance GVP modules, why are important? And when to implement?
Adverse drug reactions are a leading cause of death in hospitalized patients. Pharmacovigilance monitors medical product safety during the drug lifecycle to balance the benefits-risk ratio.
GVP modules provide essential guidelines about how pharmacovigilance will be implemented and how pharmacovigilance professionals regulate and monitor adverse effects related to medicinal products.
Do you want to learn Pharmacovigilance GVP modules in an organized and systemic way? Click here.
What is Pharmacovigilance?
Let’s discuss more details about pharmacovigilance.
- Pharmacovigilance is an exciting development in the medical industry, addressing a long-standing issue of medication adverse reactions.
- It helps ensure that all drugs and treatments are safe for use.
- By monitoring pharmaceutical products throughout their life cycle, pharmacovigilance detects potential dangerous side effects quickly and accurately so immediate action can be taken to protect patients.
- Pharmacovigilance also enables us to identify severe but rare events that may have gone unnoticed.
- Overall, this organization plays a vital role in helping society obtain reliable and effective treatments while minimizing risks.
What Are The Four Main Components Of Pharmacovigilance?
There are four major components involved in pharmacovigilance:
1- Collection of information from healthcare providers;
2- Data management from pharmaceutical companies;
3- Safety assessment by regulatory authorities; and
4- Communication with the broader public.
In the European Union, pharmacovigilance is regulated by legal obligations to ensure that only safe drugs are available to consumers.
With pharmacovigilance, we can help ensure that medications remain effective and that those taking them know what to watch out for – it’s a real backbone of modern medicine!
What Are Types Of Pharmacovigilance?
- Passive surveillance.
- Active surveillance.
- Cohort event monitoring.
- Targeted Clinical Investigations.
What Are The 6 Types Of Adverse Drug Reactions?
1- Augmented means dose-related
2- Bizarre means non-dose-related
3- Chronic means dose-related and time-related
4- Delayed means time-related
5- End of use means withdrawal
6- Failure means failure of therapy
What Is Good Pharmacovigilance Practices GVP?
Good pharmacovigilance practices GVP are a set of harmonized processes implemented to ensure the safety and efficacy of medicinal products.
GVP is designed to proactively detect, assess, understand, communicate and prevent any potential or actual adverse events related to drugs on the market.
These pharmacovigilance processes cover all stages, from initial drug authorization to post-marketing surveillance, to enhance public health protection.
At its core, GVP is about brand trust, and customer confidence – as good pharmacovigilance practices can help boost consumer satisfaction with a drug or product.
What Does GVP Stand For In Pharmacovigilance?
Through a GVP inspection, drug establishments must demonstrate adherence to post-approval regulatory requirements set out by the Good Pharmacovigilance Practices (GVP) Guidelines.
These regulations include efforts such as preparing Adverse Drug Reaction reports.
This is paramount in ensuring safety and efficacy for patients who come into contact with these drugs.
What is GVP in Clinical Trials?
GVP comprises two different processes: pharmacovigilance and risk management.
- These processes are implemented to ensure that any new pharmaceutical products have a drug safety profile before going on the market to have been deemed safe for rigorous testing and data collection.
- The good news for consumers is that GVP helps to ensure that any drugs are approved only after their safety has been verified, creating greater peace of mind for those taking them. GVP plays a significant role in keeping us safe and healthy!
What Is The Difference Between GVP and GCP?
GVP is regulations and inspections done for medicinal products after marketing approval.
GCP is regulations and inspections to monitor medical products’ safety on healthy subjects during clinical trials.
What are Regulatory Authority Expectations From Good Pharmacovigilance Practices GVP?
European Medicines Agency Expectations
In 2012, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) wanted to go above and beyond in their Good Pharmacovigilance Practices.
These activities involved enforcing stricter expectations, such as improved reporting mechanisms with the Eudravigliance database, fostering stakeholder engagement and transparency through education initiatives on a single platform, and offering scientific-backed recommendations for drug evaluation measures that benefit patients while carefully weighing possible risks.
All these collectively form an extensive scope of action compared to the FDA’s post-marketing surveillance role.
Food and Drug Administration’s Expectations
In a bold move, the EMA and FDA chose to join forces in 2014.
Through their “cluster’ relationship,” they exchange data, conduct research, and coordinate other activities, all emphasizing transparency for increased accountability.
While there is no mandatory requirement concerning post-market surveillance from the FDA regarding GVPs (Good Pharmacovigilance Practices), guidelines have been established regarding documenting safety signals and developing comprehensive case reports that meet high-quality standards.
Health Canada Expectations
In 2004, Canadian health officials began implementing Good Vigilance Practices (GVP), which established expectations for reporting adverse drug reactions and post-approval requirements.
The Health Products and Food Branch Inspectorate indicated that Market Authorization Holders must be aware of complaints procedures and report any unusual failures related to new drugs – among other things.
As such, it is paramount for healthcare workers, like pharmacists, to appraise suspected ADRs with urgency so patients can benefit from improved safety outcomes–even if a direct cause cannot conclusively be determined when filing reports.
How to Ensure GVP Compliance?
GVP pharmacovigilance guidelines have essential rules to follow.
GVP good pharmacovigilance practices are not only appropriate guidance but a must to ensure the assessment, detection, and interpretation of how medical products interact with human subjects to review risks and analyze benefits to give the best public health experience.
How?
- Meeting Specialized Work Requirements
- Delivering Expertise
- Navigating Multiple Regulatory Environments
This is done by Escalation to GPvP Compliance Management Team (CMT)
What are Pharmacovigilance GVP Modules?
GVP modules are essential to pharmacovigilance for ensuring that drugs and other medical treatments have been tested for safety and effectiveness.
The GVP module was created by the European Union in 2012 and provides mandatory information that is used in all relevant pharmacovigilance processes, including risk management plans, case processing methodology, vigilance systems’ regular checks, updates, and other aspects.
With the GVP module, healthcare professionals can ensure that their products meet the high standards of quality promised when delivering medical services.
Not only does this provide a safer environment for patients to receive their treatment, but it also helps guarantee consistency across multiple countries within the European Union.
How many modules are there in pharmacovigilance?
- GVP modules I to XVI
These are GVP modules are resposible for Pharmacovigilance.
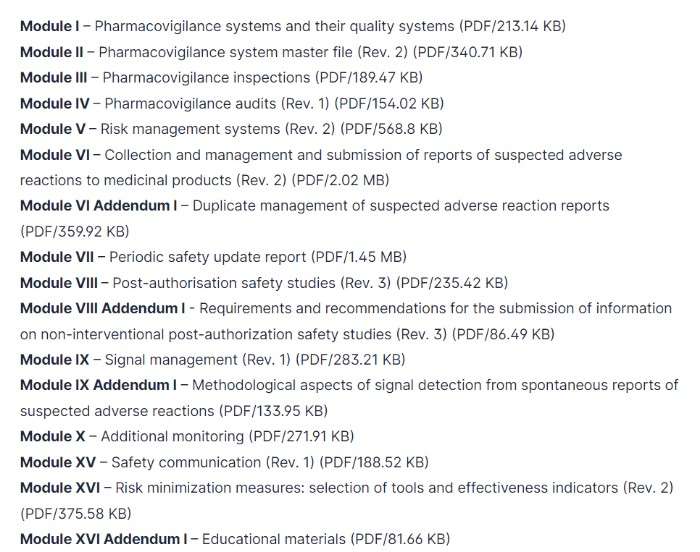
What are the Topics of GVP Modules?
According to European Medicines Agency in European Union EU, here is the GVP Module list:
What are the Most Importance GVP Guidelines?
This PDF includes a Guideline on good pharmacovigilance practices according to European Medicines Agency.
What is the GVP Job Title?
According to ZipRecruiter, the salary of the GVP role is $53,988 per year.
Most Important Terminologies Used In Pharmacovigilance
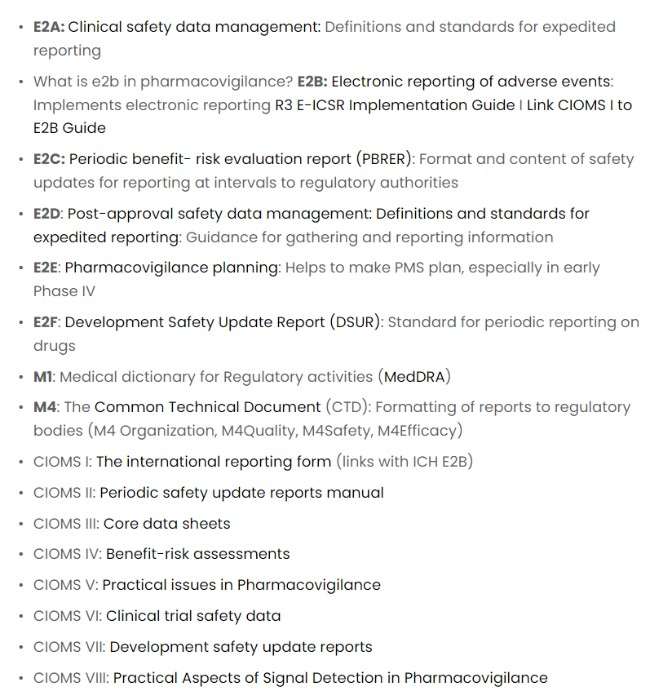
E2A is Clinical Safety Data Management.
- The ICH Harmonised Guideline of October 1994 was essential to ensure successful clinical safety reporting. This document provided clear definitions and terminology to help ensure uniformity in the field – setting standards for expedited reporting worldwide.
E2B
- E2B (R3) is the latest version of guidelines designed to ensure data transparency in individual case safety reports.
- Developed based on International standard HL 7, it allows various clinical systems to exchange information and promote patient safety worldwide seamlessly.
E2C
- A major initiative of the ICH regions is providing common standards for periodic benefit-risk evaluation on marketed products – specifically, through the E2C(R2) Periodic Benefit-Risk Evaluation Reports (PBRERs).
- These globally accepted reports are designed to ensure patient safety and product efficacy by evaluating potential threats over time.
E2D
- Pharmaceutical companies must take a vigilant approach toward benefit-risk evaluations, data management, and planning for post-approval safety.
- As part of this process, the reporting standards involve an E2C (R2) Periodic Benefit-Risk Evaluation Report, E2D Post-Approval Safety Data Management with definitions, and expedited reporting criteria Pharmacovigilance Planning via an organized deployment strategy.
E2F
- This document sets the stage for a consistent and comprehensive approach to drug safety among different ICH regions.
- It outlines what should be included in an all-encompassing Development Safety Update Report so that stakeholders can make informed decisions based on complete knowledge of the risks associated with drugs under development.
E2E
- Ensure the safety of medications with this helpful guide on pharmacovigilance planning! It provides valuable instructions for monitoring chemical entities, biotechnology-derived products, and vaccines during their early exposure to the public – helping you keep your new medicines safe.
M1
- M1 is a medical directory that is called MedDRA.
- Understanding the risk of adverse events associated with medicines is an integral part of health regulation.
- MedDRA, created by ICH, has set a new standard for how regulatory authorities can share such data – making it more accurate and efficient than ever!
M4
- M4 is The Common Technical Document (CTD) is a set of specifications for a dossier to register medicines.
- The Common Technical Document (CTD) is an internationally recognized dossier used to register medicines and ensure regulatory compliance.
- Developed by the International Conference on Harmonization of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals, this carefully crafted set of specifications has been adopted by Australia’s Therapeutic Goods Administration since 2004 – providing a safe, consistent approach to regulating medicinal products worldwide.
CIOMS I
- CIOMS, or the Council for International Organizations of Medical Sciences, is crucial in today’s pharmacovigilance landscape.
- It works to ensure the safe and effective use of medicines worldwide through its various initiatives.
- In 1986, CIOMS launched an ambitious undertaking – establishing a Working Group on International Reporting focused on unifying and streamlining adverse drug reaction reporting protocols for pharmaceutical companies submitting to regulatory authorities worldwide. This was their first step towards modernizing pharmacovigilance!
CIOMS II
- In November 1989, a pioneering initiative was launched to respond to the growing demand for periodic safety updates from multiple countries.
- To complicate matters further, each local regulatory authority had specific requirements regarding data inclusion criteria and formatting – all dependent on individual product formulations.
- This bureaucratic burden eventually led to an innovative solution that simplified report preparation by providing a standardized schedule (Fig 23.1) with readily identifiable due dates and review periods – streamlining the process across different drug substances!
CIOMS III
- The CIOMS III working group had a unique mission: to establish principles and guidelines for streamlined decision-making regarding Core Safety Information, standard terms & definitions, and the desired format.
- Their primary goal was to reduce confusion among prescribing healthcare professionals worldwide by increasing consistency in safety information across different nations and manufacturers.
CIOMS IV
- CIOMS IV guides regulatory bodies and manufacturers in assessing the risks-to-benefits ratio of newly developed or suspected products with significant safety issues.
- It outlines pragmatic approaches for reassessing said benefits, creating a comprehensive report, and developing sound decision-making practices in times of uncertainty.
- The concepts proposed by CIOMS IV are beneficial tools no matter what stage a manufacturer may be at when assessing benefit-risk factors associated with their product(s).
CIOMS V
- The CIOMS’ most ambitious initiative has addressed many issues, from modern and longstanding drug safety concerns.
- The resulting report, Current Challenges in Pharmacovigilance: Pragmatic Approaches (CIOMS, 2001), provides meaningful guidance for pharmacovigilance teams that remains relevant today.
- It offers practical solutions across topics such as collecting individual case reports over the internet and improving how deaths are reported on labels.
CIOMS VI
- Pharmacovigilance is a system that focuses on monitoring and evaluating medication safety after being released to the public.
- It aims to detect any potential adverse reactions or patient subgroups deemed particularly sensitive, leading up measures for risk management.
- CIOMS VI was established with this overall goal, considering any variations between pre-marketing trials and post-marketing surveillance.
- This also helps ensure a smooth transition from clinical trial planning through pharmacovigilance programs beyond licensure and out into everyday life use – enabling more comprehensive data analysis throughout medication development stages until release onto market shelves.
Which course is best for pharmacovigilance to learn GVP?
In our Pharmacovigilance PDFs educational materials, we have simplified GVP Modules in an easy way to read and understand, not only that but also with quizzes and checklists to implement right away after finishing reading.
FAQs
What Is The Module 7 Of GVP?
GVP Module Vii Seeks To Provide Solutions For The Difficulties Faced Since Psusa's Implementation Two Years Ago, Explaining How Best Practices Can Be Employed In Drug Safety Reporting.
What Is Psur In Pharmacovigilance?
Periodic Safety Update Reports are pharmacovigilance documents used to ensure the safety of medicinal products worldwide. They provide a comprehensive and ongoing overview detailing post-authorization developments for review by regulatory authorities at predetermined intervals.
What Is Argus In Pharmacovigilance?
With Oracle Argus, pharmaceutical companies and clinical trial organizations can gain an advantage in their safety decisions.
The platform offers the ability to optimize global compliance while integrating risk management – unlocking more incredible speed and accuracy of operations worldwide.
Which GVP Module Talks About The Pharmacovigilance System Master File?
Module II
What are A GVP Inspections?
Comprehensive Good Vigilance Practice (GVP) inspections help ensure that all drug establishments adhere to and sustain a stringent Adverse Drug Reaction management system.
To promote the effectiveness of this program, these entities must store their ADR records and annual summary reports for 25 years – allowing us to effectively monitor any adverse reactions over time while ensuring necessary label modifications take place accordingly.
What Are The Principles Of Pharmacovigilance?
Pharmacovigilance is an exciting and vital field focused on carefully monitoring medications or vaccines.
Each potential treatment goes through extensive tests to ensure it will be safe and effective before it’s approved for humans – ensuring that patients receive only quality medical treatments!
What Are The Tools Used In Pharmacovigilance?
- Oracle Argus Safety.
- ArisG.
- Oracle Adverse Event Reporting System (AERS)
- ClinTrace.
- PvNET.
- repClinical.
- Vigilanz Dynamic Monitoring System.
- WebVDME Pharmacovigilance Signal detection and Signal management software.
What Are R2 And R3 In Pharmacovigilance?
- The EMA has made substantial efforts to improve the EV system, but these have been met with technical difficulties causing additional costs and delays for marketing authorization holders.
- The significant advancement gained by transitioning from E2B(R2) to E2B(R3) is its ability to gather more comprehensive data while enabling collaboration between stakeholders through streamlined software tools to create and send electronic ICSRs.
- Assessing medical incidents has been made easier and more efficient with this innovative method.
- It allows for a comprehensive evaluation and an EU result to be provided as part of the assessment process – all based on ISO ICSR standards. By leveraging free text fields in E2B (R2) and carefully-controlled origin, methods & results within E2B (R3), gathering critical information is quicker than ever!
What Are SOPs In Pharmacovigilance?
From the foundational framework to optimize operations and ensure consistency, SOPs are a company’s tangible connection between its mission statement and daily activities.
These documents reflect an organization’s structure and reveal how individual practices combine for maximum efficiency in today’s ever-evolving workplace.
What Is ADR In Pharmacovigilance?
Adverse drug reactions have possible relation with medicinal products.
What Is Ich Guideline In Pharmacovigilance?
ICH is International Council for Harmonisation.
ICH provides a platform for international professionals and regulators to engage in lively scientific dialogue on the most effective ways of guaranteeing that drugs meant to treat humans are safe, functional, and reliable.
This conversation tests ideas from experts worldwide as they strive toward better pharmacovigilance practices.
What Are The Eight Drug Categories?
- Stimulants.
- Inhalants.
- Cannabinoids.
- Depressants.
- Opioids.
- Steroids.
- Hallucinogens.
- Prescription drugs.
What Are The Five Rs Of Drug Safety?
The right patient, the right drug, the right dose, the right route, and the right time.
What Is The First Step In Pharmacovigilance?
The first step that activates the pharmacovigilance process is detecting adverse events and the awareness by regulatory authorities’ contact points.
How Much is Pharmacovigilance Salary?
Check out this article about 143 Alternative Career Paths for Pharmacists: Top Salary in 2022(Updated)
Who Controls Pharmacovigilance?
- The Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
Who is involved in pharmacovigilance?
- Patients, healthcare professionals, governments, and pharmaceutical companies.
How Many Steps Are Involved In Pharmacovigilance?
The steps in safety data management are
- Data collection and verification
- Coding of adverse reaction descriptions
- Coding of drugs
- Case causality assessment
- Timely reporting to authorities
How to Boost the success of pharmacovigilance automation?
- Create an overall enterprise strategy.
- Start small with robotic process automation (RPA).
- Keep humans in the loop at first.
- Consider tapping more comprehensive datasets to predict future events.
- Create a framework to evaluate and explain the business case.
Which Database Is Used In Pharmacovigilance?
Oracle Argus is a market-leading pharmacovigilance database.
Resources
Good pharmacovigilance practices | European Medicines Agency
Good Pharmacovigilance Practices and Pharmacoepidemiologic Assessment | FDA
Conclusion
Pharmacovigilance is monitoring the effects of drugs after they have been marketed. It is critical to ensure that patients are safe and that pharmaceutical companies produce quality products.
Let us know if you want to learn more about pharmacovigilance or need help enacting these principles.
Pharmacovigilance PDFs educational materials are ready and waiting for you to save time and money to learn everything you need about GVP’s role in Pharmcovigoance.